In today’s article, I will talk about high availability in SharePoint 2013. High availability describes the steps you take to make your server farm resilient to hardware failures. When you are designing high availability and disaster recovery strategies for a SharePoint implementation, it is important to understand the different approaches required at each logical tiers. Designing the high availability and the disaster recovery requires careful planning and knowledge of various backup tools available.
You should protect servers against hardware failures by sourcing redundant power supply network cards, implementation RAID solution for operation system and other critical data. You can also protect the loss of an entire server by duplicating the server workloads or configuring clustering.
You can increase the number of web front-end servers to avoid loss of a WFE server and in order to offer a seamless fail-over, network load balancing can be configured.

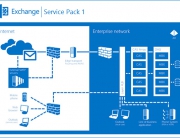
You can also protect the database servers by adding more servers running SQL Server. You should also use technologies like database mirroring, clustering and always on availability group.
SQL database mirroring is an option for making databases highly available in SQL Server. With SQL mirroring, only the principal SQL server can write changes to the database at any given time.

AlwaysOn availability groups provide high availability protection for databases by managing multiple copies of a database in a manner similar to database mirroring, but significantly enhanced.

Server virtualisation strategies can be implemented to provide high availability of SharePoint 2013 workloads.