Dec 03, 2014
Situational leadership is a leadership model developed by Hersey and Blanchard. A situational leader is one who can adopt different leadership styles depending on the task readiness of the team member. The Situational Leadership model addresses four types of situations:- Situation 1: Directing – ‘I’ll decide.’
- Situation 2: Coaching – ‘We’ll talk, I’ll decide.’
- Situation 3: Supporting – ‘We’ll talk. We’ll decide.’
- Situation 4: Delegating – ‘You decide. I’ll be available.’
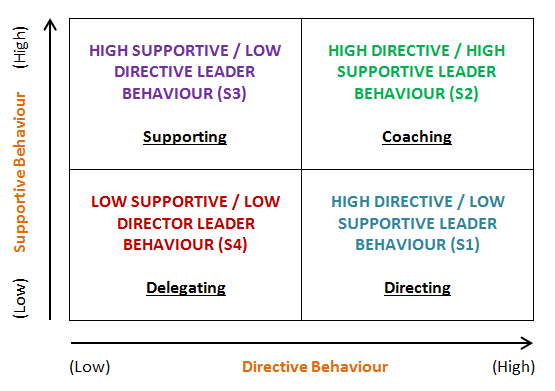
- Team member: low competence, low commitment, not confident/unable and unwilling or insecure.
- Situational leader: high task focus, low relationship focus, key behaviour: telling.
- Team member: some competence, variable commitment, unable but willing.
- Situational leader: high task focus, high relationship focus, key behaviour: explaining.
- Team member: high competence, variable commitment, able but unwilling.
- Situational Leader: low task focus, high relationship focus, key behaviours include supporting and encouraging.
- Team member: high competence, high commitment, able and willing.
- Situational Leader: low task focus, low relationship focus, key behaviour: delegating.
The task-readiness level of each team member for each task provides the answer. Hersey and Blanchard suggest that a leader’s style should vary according to each team member’s task-readiness level. Two things make up a team member’s task-readiness level. The first is their competence, or ability to do a particular task. Competence is a combination of skills, knowledge and experience in doing a particular task. The second is their willingness to take responsibility for doing the task. This is a combination of motivation and self-confidence. Please remember the concept of task-readiness level can relate to one task only, not to people’s overall competence for their job as a whole. This means that a team member’s task readiness level can be high on some tasks (Situation 4) and low on others (Situation 1). Therefore the Situational Leader will use different situational leadership styles with the team member for different tasks.So there you have it, a leadership model where the ultimate goal is to develop all of your team members to the delegating level so that you and your family can spend more time watching more sunsets together. This also means your team members can become all that they can become because they are led by a situational leader. To learn more about how to become a situational leader and other areas of leadership, take a look at New Horizons’ Management and Leadership training programs. Take good care and ‘enjoy’ today because ‘tomorrow’ is promised to none of us.
How do your Excel skills stack up?
Test NowNext up:
- Save time with print presets in Adobe InDesign CS6
- Normalising your database: First Normal Form (1NF) – Part 1
- Change the Spell Check Language on all slides in PowerPoint using VBA (2007 onwards)
- Fruitcakes and lines in the sand
- The changing face of the Office 365 plans
- Two ways to put a sticky note on your desktop
- Excel formulas are not just for numbers
- Our interpersonal rights and responsibilities in the workplace
- Implementing external content types in SharePoint 2013
- Happy Holidays from New Horizons!
Previously
- Using the ‘Flash Fill’ feature to apply the desired formatting in Excel 2013
- ‘CONNECT ANY DATABASE’ in SQL Server 2014
- Scheduling Rostered Days Off (RDO) in Project 2013
- Apply permissions on web parts in SharePoint
- Fabulous, fitting feedback
- Comparing and combining two lists using VLOOKUPs
- The Windows Server 2012 R2 Desktop Experience
- Removing the background from a picture in Microsoft Office
- Deliver successful organisational transformation
- Using SharePoint to create a ‘Team Based Master Calendar’